Category

Solenoid Valve Supplier
Home » Pneumatic Solenoid Valves » 5/2 Way Pneumatic Solenoid Valve for Double Acting Cylinder
5/2 Way Pneumatic Solenoid Valve for Double Acting Cylinder
The two-position five-way solenoid valve is usually used with a double-acting pneumatic actuator. The valve body has five air connection ports, one of which is connected with air source, two with double-acting cylinders of actuators and two of which are exhaust ports.
Double-acting pneumatic actuator means that both sides of the cylinder piston need air pressure to push the piston. When there is pressure on one side of the piston and there is no pressure on the other side, the piston will move to the side with low pressure, and the cylinder will generate a thrust in one direction. When the pressure on one side of the piston with air pressure disappears, the pressure on the other side without pressure is added to the pressure of the source, and the piston will move back, and the cylinder generates a return thrust. By repeatedly switching the air pressure at both ends of the piston, the cylinder generates reciprocating motion. Dual-acting cylinder is not normal, so its position is uncertain without any compressed air.

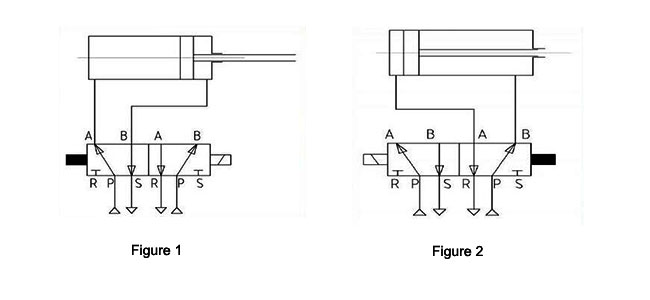
2-position 5-way single solenoid valve for the double-action air cylinder
1. Initial state
The solenoid valve is disconnected with power, and Port P and A of solenoid valve are connected. The air supply enters the left chamber of the pneumatic piston driving part via Port A, and the piston stops on the right side. Port B and Port S are connected, and the right chamber in the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port B is at an exhaust state. See Fig. 1 below.
2. Working state
The solenoid valve is connected with power. The solenoid valve port A and port B are connected. The air supply enters the right chamber of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port B. The piston moves to the left side. Port A and Port R are connected. The left chamber of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port R is at an exhaust state. See Fig. 2 below.
3. Power-off state
The solenoid valve resumes to its initial state. See Fig. 1.
 2-position 5-way double solenoid valve for the double-action air cylinder
2-position 5-way double solenoid valve for the double-action air cylinder
When the left coil is connected with power, the Port P and A of solenoid valve are connected. The air supply enters the chamber on one side of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port A to move piston to the other side of the air cylinder. Port B and Port S are connected. The chamber on the other side of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port B is at an exhaust state.
When the right coil is connected with power, the solenoid valve port P and B port are connected. The air supply enters the chamber on one side of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port B to move piston to the other side of the air cylinder. Port A and Port R are connected. The chamber on one side of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port A is at an exhaust state. The coil on the other side which is disconnected with power remains the current state unchanged. See Fig. 2 below.
Double-acting pneumatic actuator means that both sides of the cylinder piston need air pressure to push the piston. When there is pressure on one side of the piston and there is no pressure on the other side, the piston will move to the side with low pressure, and the cylinder will generate a thrust in one direction. When the pressure on one side of the piston with air pressure disappears, the pressure on the other side without pressure is added to the pressure of the source, and the piston will move back, and the cylinder generates a return thrust. By repeatedly switching the air pressure at both ends of the piston, the cylinder generates reciprocating motion. Dual-acting cylinder is not normal, so its position is uncertain without any compressed air.

2-position 5-way single solenoid valve for the double-action air cylinder
1. Initial state
The solenoid valve is disconnected with power, and Port P and A of solenoid valve are connected. The air supply enters the left chamber of the pneumatic piston driving part via Port A, and the piston stops on the right side. Port B and Port S are connected, and the right chamber in the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port B is at an exhaust state. See Fig. 1 below.
2. Working state
The solenoid valve is connected with power. The solenoid valve port A and port B are connected. The air supply enters the right chamber of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port B. The piston moves to the left side. Port A and Port R are connected. The left chamber of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port R is at an exhaust state. See Fig. 2 below.
3. Power-off state
The solenoid valve resumes to its initial state. See Fig. 1.

When the left coil is connected with power, the Port P and A of solenoid valve are connected. The air supply enters the chamber on one side of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port A to move piston to the other side of the air cylinder. Port B and Port S are connected. The chamber on the other side of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port B is at an exhaust state.
When the right coil is connected with power, the solenoid valve port P and B port are connected. The air supply enters the chamber on one side of the double-action pneumatic piston driving part via Port B to move piston to the other side of the air cylinder. Port A and Port R are connected. The chamber on one side of the pneumatic piston driving part connected with Port A is at an exhaust state. The coil on the other side which is disconnected with power remains the current state unchanged. See Fig. 2 below.

Post a Comment:
You may also like: